Theme: Explore the latest trends in Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry
Bioorganic Medicinal 2018
- About Conference
- Scientific Sessions / Tracks
- Market Analysis Report
- New Updates:Medicinal Chemistry &Pharmaceutical Chemistry
- Past Conference Report
BIOORGANIC MEDICINAL 2018
Bioorganic Medicinal 2018 welcomes all the attendees, speakers, sponsors and other research expertise from all over the world to the World Congress on Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry which is going to be held during November 12-13, 2018 in Dubai, UAE.

Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry 2018 focus to bring together leading academic scientists, speakers, researchers and research scholars to exchange and share their experiences, ideas and research results on all aspects of Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry. It can also provide a premier interdisciplinary platform for researchers, practitioners and educators to present and discuss the most recent innovations, trends, and concerns as well as practical challenges encountered and solutions adopted in the fields of Medicinal Chemistry, Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Analytical Chemistry, Stereochemistry, Veterinary and Human Medicine.
Why Attend?
Bioorganic Medicinal 2018 is an international event focusing on the core knowledge and major advances in the ever-expanding field of Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry by attracting experts on a global scale. It is a global platform to discuss the innovative researches and developments in the Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry. It will be a golden opportunity to meet eminent personalities and to learn the latest technological advancements.
Who Attends?
Chemist
Researchers
Pharmaceutical Industry Professionals
Academicians
Associations and Societies
Post-Doctoral Fellows
Young Researchers
Doctors
Government Agencies
Clinical Toxicologists
Clinical Pharmacologists
Education providers
Pharmacologists
Healthcare professionals Professors
Researchers
Pharmacists
Pharmacy Technicians
Chemistry Specialists
Why Dubai?
Dubai is a city which is located in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The emirate of Dubai is located on the southeast coast of the Persian Gulf and has the largest population in the UAE (2,106,177) and the second-largest land territory by area (4,114 km2) after Abu Dhabi. There are 52 institutions in Dubai that offer higher education programs.
And they are grouped into three categories: Federal institutions, Institutions in the Free Zones and Institutions outside the Free Zones. The most popular field of study among students in Dubai is Business (42% of students), followed by Society, Law, and Religion (19%). Significant numbers are also studying Engineering (9%), Information Technology (6%) and Media and Design (7%). There are very few students studying Health and Medicine (2%), Education (1%), Natural and Physical Sciences (1%) and Tourism and Hospitality (1%). Around 7% of all students are in Foundation programs that prepare school leavers with necessary skills for university study.
Track 1: Structural & Molecular Biochemistry
Structural Biochemistry is a sub-division of biochemistry that mainly focuses on the structural characteristics of the molecules within cells and other made up of living organisms. The main area is focused on the structural basis of fundamental biological processes. It involves the study of the structure of macromolecules. It includes methods for structure determination and huge data of structural information. Additionally deals with the interactions amongst totally different cell parts as well as macromolecules like nucleic acids, proteins, lipids, amino acids, and carbohydrates. Molecular biochemistry has big wide to capture the array of chemistry, physics, medicine, and biology.
-
Translation science
-
Nucleic acid biochemistry
-
Lipids biochemistry
-
Structural Alignments
-
Biomolecular structure and function
-
Enzymology
Track 2: Biological Drug Targets
The term biological target is also used in pharmaceutical research to describe the natural protein in the body whose activity is modified by a drug resulting in a specific effect at the specific site, which may be an adequate therapeutic effect or an unnecessary adverse effect. Biological target identification and validation are some of the maximum essential steps in developing a new drug. Drug target validation includes proving that DNA, RNA, or a protein molecule is at once concerned in an ailment process and may be an appropriate goal for the improvement of a brand new therapeutic drug. Targeted drug delivery systems have been developed to optimize regenerative methods.
-
Nucleic Acids
-
G-protein coupled receptors
-
Liposomes
-
Nanoparticles
-
Biodegradable Polymers and non-biodegradable polymers
Track 3: Drug Design and Development
Drug discovery and design are the processes of finding new drugs by design, depending on their biological targets. It is also known as a rational drug design. Drug discovery is an effort to develop a new drug molecule by applying varieties of methodologies of design. This procedure includes the identification of drug targets, candidates, Synthesis, Screening, physical and chemical characterization and assays. Drug development is the process of manufacturing and marketing the biologically active compound by drug design by observing the pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, toxicological and various clinical parameters are included.
-
Structural based drug design
-
The neural network in drug design
-
Clinical drug development
-
Risks associated with new drug development
-
Rational drug design techniques
Track 4: Drug Delivery Techniques
Drug delivery is the method of intended a pharmaceutical compound to develop a therapeutic effect for human or animal use. It is an integrated concept with dosage form and route of administration. Nasal and pulmonary routes of drug delivery techniques are gaining importance for the treatment of human diseases. These methods are concerned with the drug release profile, absorption, distribution and elimination for the advancement of the product viability and safety and patient convenience and compliance. To lower the drug degradation, adverse effects, and side effects. To increase drug bioavailability and bioequivalence to prevent harmful toxic-effects. Many drug delivery and drug targeting techniques are currently under development.
-
Polymeric drug delivery technique
-
Drug delivery using Nanotechnology
-
Transdermal drug delivery system
-
Novel drug delivery system
-
Bio-adhesive drug delivery system
Track 5: New Trends in Medicinal Pharmacy
Current advancement in Medicinal Pharmacy efforts is moving towards the more targeted approach. Target identification and validation are the first major stages of this process. It involves demonstration of relevance and confirmation of target protein in a disease which can then be translated to animal models and this may involve the latest in gene expression techniques and gene targeting methods. An advance in Medicinal pharmacy covers the principles, methods, and technologies that the pharmaceutical industry uses to turn that candidate molecule into the final drug dosage form. Optimizing the therapeutic performance of the molecule which includes designing, characterizing, testing the drug in clinical trials, and manufacturing the final product.
-
Super-enhancers that control cell state and identity
-
Clinical trials and drug research
-
Narrow artificial intelligence
-
Nutritional genomics
Track 6: Global Chemical Analysis
The global chemical industry is very large and competitive. The industry products account for a major share of the overall global chemicals industry. The global chemical industry consists of a very diverse and complicated range of products. In terms of revenue, it is one of the world’s largest markets World Congress on Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry 2018 welcomes all the leading industries and eminent leaders to join us and share their ideas for enhancing the market of Chemical Industry and factors affecting the strength of competition in the global chemicals market.
-
Increasing of global chemical industry revenue growth
-
Forecast Global organic chemicals market value
-
Factors influencing the global chemical market
-
Enhancing the Production value of the chemical manufacturing industry
Track 7: Organic Chemistry in today’s life
Carbon is one of the unique element to form a wide variety of compounds that contain long chains and/or rings of carbon atoms. Organic molecules are the most complex chemical structures found in living organisms. Despite their size and complexity, these biological molecules follow the same chemical principles as simpler organic molecules. Organic chemistry is that the study of chemical compounds containing a minimum of one bond between an atom of a chemical compound and a metal complex. Organic chemistry combines aspects of Bioorganic Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry, and Medicinal Chemistry. Organic chemistry unit of measurement is widely used in the same chemical process. The carbon atoms combine with other elements in a number of different ways to through special bonds like covalent bonds to form a large number of compounds which have a strong influence on nature, and specific behavior and properties can be applied to medical, health, industrial and commercial fields. Organic chemistry mainly aims to provide progress in the fields of Medicinal chemistry, Forensic chemistry, Asymmetric synthesis, organometallic chemistry, bioorganic chemistry, Heterocyclic chemistry and Analytical methods of Inorganic chemistry.
-
Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry
-
Chemistry of DNA and RNA
-
Science advances through interaction
-
Organic chemistry and industry
Track 8: Medicinal Chemistry
Medicinal chemistry and pharmaceutical chemistries are disciplines at the intersection of chemistry, especially synthetic organic chemistry, and pharmacology and various other biological specialties, where they are involved with design, chemical synthesis and development for the market of pharmaceutical agents or bioactive molecules. It involves chemical aspects of identification, and then systematic through synthetic alteration of new chemical entities to make them suitable for intended use. At the biological interface, Medicinal chemistry combines to form a set of highly interdisciplinary organic, physical computational emphases alongside biological areas.
-
Toxicological studies
-
Organic Chemistry
-
Pharmacognosy
-
Veterinary and human medicine
-
Pharmacy Practice
Track 9: Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacokinetic is the quantitative analysis of drug movement in, through and out of the body. The intensity of the effect is related to the concentration of the drug at the site of action. Pharmacokinetics also includes the study of the time course of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. Clinical pharmacokinetics is the application of pharmacokinetic principles to the safe and effective therapeutic management of drugs in an individual patient. Primary goals of clinical pharmacokinetics include enhancing safety, efficacy and reducing the toxicity of a patient’s drug therapy. The development of strong correlations between drug concentrations and their pharmacologic responses has enabled clinicians to apply pharmacokinetic principles to actual patient situations.
Pharmacodynamics is the study of the physiological and biological effect of drugs. The effect of a drug present at the site of achievement is determined by that drug’s binding to a receptor. Receptors may be present on neurons in the central nervous system to depress pain sensation, on cardiac muscle to affect the intensity of contraction, or even within bacteria to disrupt maintenance of the bacterial cell wall.
-
Metal complexes in medicine
-
Bioorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry
-
Kinetics of drug action in disease
-
Therapeutic drug monitoring
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetics
-
Variation in chemical diversities in drugs
Track-10: Computational Chemistry
Computational chemists develop and apply computer programs to answer key questions in biochemistry. They model, predict, visualize, and analyze the structures, functions, and interactions of biologically important molecules. Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses computer simulation to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses methods of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and atoms.
-
Discovery of biomolecules through metagenomics
-
Synthetic biology
-
Genome Analysis
-
Chemical and Molecular dynamics
-
Proteogenomics
Track-11: Pharmaceutical Chemistry
Pharmaceutical chemistry is the study of drug compounds, and it involves drug development process. This includes drug discovery, delivery, absorption, metabolism, distribution, and excretion. There are elements of biomedical analysis, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. Pharmaceutical chemistry work is usually done in laboratory conditions it mainly involves cures and remedies for disease, analytical techniques, pharmacology, metabolism, quality control, quality assurance, and drug chemistry. Pharmaceutical chemistry leads to careers in drug development, pharmaceutical industries, and research facilities. Pharmaceutical chemists are involved in the development and assessment of therapeutic compounds. Every chemical that is synthesized must be tested for biological activity. In vitro testing involves biological assays outside a living system that means in laboratory conditions. The field of pharmaceutical chemistry is unique and it involves vast areas of expertise. Analytical chemists can isolate and identify active components from the plant and other natural resources. Pharmaceutical chemists evaluate the bioactivity of drugs and drug metabolites. Pharmacologists can assess drug purity, safety and efficacy adverse effects of drug therapy. When a drug has been approved for human studies, clinicians and physicians should monitor patient’s compliance with treatment with the new drug compound. The impact of pharmaceutical chemistry in the development of drug compounds is very high and advanced methods are now available for development of the drug by using pharmaceutical chemistry are
-
Molecular modeling based drug design system
-
Advanced organic synthesis techniques
-
In-vitro safety studies
-
Analytical method development
-
Metabolic stability studies
-
Screening of drug candidates and lead molecules
Track 12: Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry
Bioorganic chemistry is a scientific subject that combines both natural chemistry and biochemistry whereas Medicinal chemistry is the field which specializes in small natural molecules that encompasses synthetic natural chemistry and elements of herbal products and computational chemistry in close combination with enzymology, chemical and structural biology, together aiming on the development and discovery of new healing agents. Organic chemistry is used to explain how enzymes catalyze the reactions of metabolic pathways and why metabolites react the manner they do. It is focusing to expand organic-chemical research on structures, synthesis, and kinetics in a biological direction.
-
Drug-receptor interaction
-
Electrochemistry in drug discovery
-
Herbal plant products and nutraceuticals
-
Drug discovery in autoimmunity
Track 13: Organic Chemical Engineering
Organic chemical engineering is a branch that applies physical sciences (physical science and organic natural science), life sciences (microbiology and organic chemistry), together with connected arithmetic and financial matters to deliver, change, transport, and appropriately utilize chemicals and materials.
-
In-vitro safety studies
-
Biochemical engineering
-
Catalysis and reaction engineering
-
Materials science
Track 14: Medicinal Biochemistry
Medicinal biochemistry is that branch of drugs involved with the biochemistry and metabolism of human health and sickness. The medical chemist is trained in the operation and management of clinical biochemistry laboratories. The medical chemist directs clinical laboratories, consults, diagnoses and treats patients with a range of metabolic disorders and biochemical abnormalities. Medicinal biochemistry deals with the functioning of traditional and pathologic organisms from a biochemical purpose of view. It provides a whole understanding of all chemical processes occurring and related to living cells at the molecular level that's associated with drug action. It conjointly helps to acquire data on the adverse effects, molecular targets, & characterization of medicine or different chemical substance within the living cells & organisms.
-
Protein structure and dynamics
-
Forensic biochemistry
-
Pharmacokinetics
-
Pharmacodynamics
-
Characterisation of medicine
Track 15: Chemical Biology
Chemical biology is the study of the chemicals and chemical reactions involved in biological life processes, incorporating the disciplines of bioorganic chemistry, biochemistry, cell biology, and pharmacology. Chemicals including natural small molecules, such as lipids, carbohydrates, and metals, or non-natural probe or drug molecules are used to gain insight into biological problems at a mechanistic level. There are some biological problems demand molecular and quantitative answers that can only be supplied by tools and approaches derived from chemistry such as single-molecule measurements, single-cell imaging, and the use of exogenous molecules to modulate the activity of cellular components. While yeast metabolic engineering has focused on assembling pathways in the cell cytosol.
-
Proteomics
-
Molecular sensing
-
Discovery of biomolecules through metagenomics
-
Chemical approaches to stem-cell biology
Importance & Scope:
The significance of recent trends reviews the state of the art and aims to determine the significance of technology and market trends in Bio-organic and medicinal chemistry for advancing productivity in drug discovery. One, in particular, fragment-based drug design, stands out as promising major improvements in research productivity. After analysis, it proves that Bio-organic and medicinal chemistry-related approaches and methodologies that drug discovery organizations employ in an effort to enhancing productivity in early drug discovery. Its major topics considered include structure-based drug design, fragment-based drug design, natural products-based drug design, diversity-oriented synthesis, and chemogenomics. Various ways of computer-aided drug design are also considered, as the complexity and limitations of drug discovery programs that are based on biochemical screens of large compound collections have been major factors in stimulating the growth of this modality.
Why Dubai, UAE?
Dubai pharmaceutical giant maintained a robust lead over drug makers in our annual ranking of the largest Bio-Pharma companies in the United States of America.
However, the pharmaceutical market is still dominated by a few very large companies that control the import/distribution, retail, and manufacturing sectors. While these companies have played an important role in the pharmaceutical sectors. Dubai market dominance leads to high markup for medicines which explain the high expenditures on pharmaceuticals.
Conference Highlights:
-
Organic Chemical Engineering
-
Organic Chemistry and Organic Chemistry in today’s life
-
Global Chemical Analysis
-
Current trends in Medicinal Pharmacy
-
Techniques in Drug Delivery
-
Identification of Drug, Design, and Development
-
Biological Target Techniques
-
Medicinal Biochemistry
-
Computational Chemistry and Chemical Biology
-
Structural and Molecular Biochemistry
-
Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics
Why attend?
Meet your target market with members from around the world focused on learning about advertising and marketing, this is your single best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from all over the world. Conduct demonstrations, distribute information, meet with current and potential customers, make a splash with a new product line, and receive name recognition at this 3-day event. World-renowned speakers, the most recent techniques, tactics, and the newest updates in advertising and marketing fields are hallmarks of this conference.
A Unique Opportunity for Advertisers and Sponsors at this International event
Major Marketing Associations around the Globe
-
American Association for Clinical Chemistry
-
American Chemical Society
-
American Institute of Chemists (AIC)
-
American Society of Brewing Chemists
-
Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC)
-
Swedish Chemical Society
-
New Swiss Chemical Society
-
Syngenta, Hyderabad Area, India
-
DCTG, Beijing City, China
Major Marketing Associations in the USA
-
American Association for Clinical Chemistry
-
American Chemical Society
-
American Institute of Chemists (AIC)
-
American Society of Brewing Chemists
-
American Society for Mass Spectrometry
The United States is the largest market for pharmaceuticals accounting for around 35 percent of the global market and is the world leader in biopharmaceutical research and development (R&D). According to the Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers Association (PhRMA), U.S. firms conduct the majority of the world's research and development in pharmaceuticals and hold the intellectual property rights on most new medicines. The biopharmaceutical sector accounts for the largest single share of all U.S. business research and development (R&D) investment, representing 23.4 percent of all domestic R&D funded by U.S. business in 2013.
More than 854,000 people work in the biopharmaceutical industry in the United States across a broad range of occupations, such as scientific research, technical support, and manufacturing. Directly and indirectly, the industry supports a total of 4.4 million jobs across the United States and added an estimated $1.2 trillion in economic output in 2014, representing 3.8 percent of total U.S. output.
U.S. generic drug sales reached an estimated $70 billion in 2015, representing a quarter of the global market, due to a large number of drugs going off-patent and healthcare reforms favoring generics. OTC market growth will be driven by a growing aging population, consumer trends towards self-medication, and the conversion of drugs from prescription to non-prescription or OTC status.
The United States has one of the world’s most supportive domestic environments for the development and commercialization of pharmaceuticals with minimal market barriers. Its strengths include an intellectual property system that rewards innovation through patent and data protection, a science-based regulatory system that is considered the most rigorous in the world, the world’s largest scientific research base fostered by academic institutions and decades of government research funding, and robust capital markets. The United States attracts the majority of global venture capital investments in start-up biopharmaceutical enterprises.
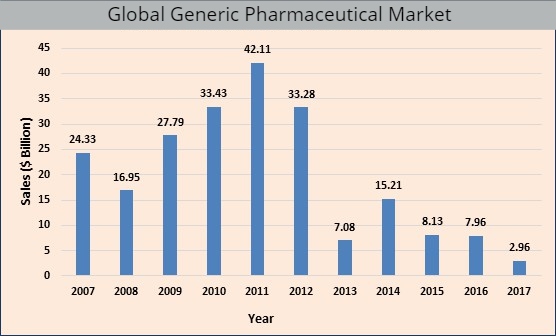
Global Generic Pharmaceutical Market Analysis:
RELATED CONFERENCES
-
Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry Conferences, July 19-21, 2018 Dubai, UAE
-
Chemistry in Drug Discovery & Designing Congress, April 16-17, 2018 Dubai, UAE
-
Food Chemistry & Food Microbiology Congress, September 03-04, 2018 Dubai, UAE
-
Medicinal Plants, Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry and Natural Products Conferences, October 30-31, 2018 Dubai, UAE
-
Pharmacovigilance & Clinical Trials Summit, July 09-10, 2018 Sydney, Australia
-
Drug Discovery Congress, October 09-10, 2017, USA
-
Drug Discovery Chemistry Conferences, April 02-06, 2018 San Diego, USA
-
Drug Discovery Summit, June 2018, Berlin, Germany
-
Discovery Chemistry & Drug Design Congress, June 2018, Berlin, Germany
-
Pharmaceutical Sciences and Innovations in PharmaIndustry Congress, February 26-27, 2018 London, UK
-
Pharmaceutical Development and Technology Conferences May 11-12, 2018 Tokyo, Japan; Barcelona, Spain
-
Medicinal and Natural Products Chemistry Conferences, February 27-28, 2018 Barcelona, Spain
-
Pharmaceutics & Drug Delivery Systems Congress, September 20-22, 2018 Prague, Czech Republic
-
Phytochemistry and Medicinal Plants Conferences, March 29-30, 2018 Sydney, Australia
-
Structural Biotechnology and Medicinal Chemistry Conferences, July 23-24, 2018 Rome, Italy
-
Bioorganic Chemistry and Applications Conferences, February 15-16, 2018 Istanbul, Turkey
-
Organic Materials Chemistry and Bioorganic Chemistry Conferences, January 18-19, 2018, London, UK
-
Bioorganic Chemistry and Natural Product Synthesis Conferences, February 15-16, 2018 London, UK
-
Medicinal Chemistry Conferences, January 18-19, 2018 London, UK
-
Bioorganic Chemistry: Methods and Applications Conferences, February 19-20, 2018 Paris, UK
-
Medicinal Chemistry and Bio pharmaceutics Conferences, January 18-19, 2018 London, UK
-
Bio based Chemicals and Medicinal Chemistry Conferences, January 25-26, 2018 Paris, UK
-
Peptide Chemistry and Medicinal Application Conferences, February 19-20, 2018 Paris, UK
-
Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Design Conferences, July 19-20, 2018 Paris, UK
-
Drug Design, Medicinal Chemistry and Pharmacogenetics Conferences, July 26-27 2018 London, UK
-
Medicinal Chemistry, Drug Discovery and Antineoplastic Drugs Conferences, October 15-16, 2018 London, UK
-
Applied Pharmaceutical Chemistry Conferences, February 15-16, 2018 Istanbul, Turkey
RELATED SOCIETIES
USA
1. US Chemistry departments and association
2. American Association for the Advancement of Science
3. American Chemical Society
4. American Institute of Chemical Engineers
5. American Institute of Chemists
6. American Association for Clinical Chemistry
7. American Oil Chemists Society
8. Brazilian Chemical Association
9. Brazilian Society of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics
10. Mexican Chemical Society
11. The Electrochemical Society
12. Society of Chemical Manufacturers and Affiliates
EUROPE
1. European Association for Chemical Sciences
2. European Association of Employed Community Pharmacists in Europe
3. European Chemical Society
4. European Pharmaceutical Union
5. New Swiss Chemical Society
6. Association of the Scientific Medical Societies in Germany
7. Austrian Pharmacological Society
8. Canadian Pharmacists Association
9. Canadian Society of Clinical Chemists
10. Chemical Institute of Canada; Czech Chemical Society
11. Federation of African Societies of Chemistry
12. Italian Chemical Society
13. Pan Africa Chemistry Network
14. Pharmaceutical Group of the European Union
15. South African Chemical Institute
16. Royal Netherlands Chemical Society
17. Slovak Chemical Society
18. Slovenian Chemical Society
19. Association of Greek Chemists
20. Latvian Chemical Society
21. International Isotope Society
22. Swedish Chemical Society
23. Croatian Chemical Society
24. Danish Chemical Society
25. Estonian Chemical Society
26. Society of Chemical Industry
27. The European Federation for Medicinal Chemistry
28. Hungarian Chemical Society
29. Institute of Chemistry of Ireland
ASIA-PACIFIC
1. Chinese-American Chemical Society
2. Chinese Chemical Society
3. Chemical Research Society of India
4. Chemical Society of Japan
5. Chemical Society of Thailand
6. Chemical Society of the South Pacific
7. Chinese Chemical Society
8. Chinese Pharmaceutical Association
9. Chinese-American Chemical Society
10. Chemical Society of Turkey
11. Hong Kong Chemical Society
12. Japan Association for International Chemical Information
13. Pharmaceutical Society of Australia
14. Royal Australian Chemical Institute
15. Pharmaceutical Society of Australia
16. Chemical Society of Vietnam
17. New Zealand Institute of Chemistry
18. The Korean Chemical Society
19. World Association of Theoretical and Computational Chemists
20. Institute of Chemistry, Ceylon
MIDDLE EAST
1. Kuwaiti Chemical Society
2. Chemical Information Professional associations serving Oman
3. Saudi Society for Clinical Chemistry
4. Saudi Society for Clinical Laboratory Sciences
5. The Israel Chemical Society.
TOP UNIVERSITIES IN USA
-
Harvard University
-
Stanford University
-
Yale University
-
Columbia University
-
University of California--Los Angeles
-
Duke University
-
University of Pennsylvania
-
University of California
-
University of Pittsburgh
-
University of Michigan
-
Johns Hopkins University
-
New York University
-
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
-
University of Minnesota--Twin Cities
-
University of North Carolina--Chapel Hill
-
Washington University in St. Louis
-
University of California--Berkeley
-
University of Washington
-
University of Chicago
-
Cornell University
-
Vanderbilt University
-
University of California--San Francisco
-
University of California--Davis
-
Northwestern University
-
Princeton University
-
Emory University
-
University of Wisconsin—Madison
-
Ohio State University--Columbus
-
Boston University
-
Pennsylvania State University--University Park
-
University of Texas--Austin
-
University of Virginia
-
University of Rochester
-
University of California--Irvine
-
Brown University
-
University of Southern California
-
Michigan State University
-
University of Iowa
-
University of Maryland--College Park
-
Arizona State University--Tempe
-
Stony Brook University--SUNY
-
Indiana University--Bloomington
-
Mount Sinai School of Medicine
-
University of Miami
-
Florida State University
-
University of Arizona
-
University of Colorado--Boulder
-
Carnegie Mellon University
-
University of Illinois--Chicago
-
Dartmouth College
-
University of Missouri
-
University of Oregon
-
University of Florida
-
Purdue University
-
University of California
-
University of Connecticut
-
University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center--Dallas
-
The State University of New Jersey
-
Texas A&M University--College Station
-
Yeshiva University
-
Baylor College of Medicine
-
University of Maryland--Baltimore
-
University of Utah
-
Tufts University
-
University of Cincinnati
-
University of South Florida
-
University of New Mexico
-
University of Kansas
-
Temple University
-
Case Western Reserve University
-
University of California--Riverside
-
University of Georgia
-
University of Notre Dame
-
University of Kentucky
-
Medical University of South Carolina
TOP UNIVERSITIES IN EUROPE
-
King's College London
-
University College London
-
University of Oxford
-
University of Cambridge
-
Karolinska Institute
-
University of Amsterdam
-
VU University Amsterdam
-
Catholic University of Leuven
-
University of Groningen
-
University of Munich
-
Maastricht University
-
Radboud University Nijmegen
-
Aarhus University
-
Ghent University
-
University of Zurich
-
University of Barcelona
-
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
-
Technical University of Dresden
-
Cardiff University
-
University of Copenhagen
-
Heidelberg University
-
University of Manchester
-
University of Edinburgh
-
Freie Universität Berlin
-
Leiden University
-
University of Bristol
-
University of Basel
-
Erasmus University Rotterdam
-
University of Geneva
-
Tilburg University
-
University of Sussex
-
Birkbeck University London
-
University of Oslo
-
Eberhard Karls University, Tübingen
-
Imperial College London
-
University of Exeter
-
Paris Descartes University-Paris V
-
University of Bern
-
University of York
-
University of Birmingham
-
University of Southampton
-
University of Bonn
-
Newcastle University
-
University of Cologne
-
Charite - Medical University of Berlin
-
University of Warwick
-
Sapienza University of Rome
-
University of Helsinki
-
Autonomous University of Barcelona
-
University of Göttingen
-
University of Nottingham
-
University of Glasgow
-
University of Würzburg
-
University of Padua
-
University of Leipzig
-
University Catholique of Louvain
-
Technical University of Munich
-
Philipps University of Marburg
-
University of Konstanz
-
University of Leicester
-
University of Freiburg
-
Trinity College Dublin
-
University of Gothenburg
-
University of Kent
-
United Kingdom Canterbury, Kent
-
University of Milan - Bicocca
-
Uppsala University
-
University of Turku
-
University of Hamburg
-
London School of Economics and Political Science
-
University of Bergen
-
University of Leeds
-
University of Sheffield
-
Medical University of Vienna
-
University of Bologna
-
University of Münster
-
Friedrich Schiller University of Jena
-
Linköping University
-
Pierre and Marie Curie University
-
Lund University
-
Durham University
-
University of Lausanne
-
Johann Wolfgang Goethe University Frankfurt am Main
-
Stockholm University
-
University of Valencia
TOP UNIVERSITIES IN MIDDLE EAST
-
Mohammed bin Rashid University of Medicine and Health Sciences
-
Gulf Medical University
-
United Arab Emirates University
-
University of Sharjah
-
King Saud University
-
Cairo University
-
King Abdulaziz University
-
American University of Beirut
-
Qena Faculty of Medicine
-
Kasr El-Aini Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University
-
Ain Shams University Faculty of Medicine
-
Alexandria Faculty of Medicine
-
Mansoura Faculty of Medicine
-
Mansoura Manchester Medical Programme
-
Faculty of Medicine Zagazig University
-
Benha Faculty of Medicine, Benha University
-
Fayoum Faculty of Medicine
-
Assiut Faculty of Medicine
-
Suez Canal Faculty of Medicine
-
Minia Medical School
-
Monofia Faculty of Medicine
-
Sohag Faculty of Medicine
-
Tanta Faculty of Medicine
-
Alfaisal University
-
Ain Shams University
-
Mansoura University
-
Université de Tunis El Manar
-
King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences
-
United Arab Emirates University
-
Kuwait University
-
Assiut University
-
Université de Monastir
-
Université de Sfax
-
Sultan Qaboos University
-
Jordan University of Science & Technology
-
Minia University
-
King Khalid University
-
University of Tanta
-
Al Azhar University
-
Zagazig University
-
University of Balamand
-
University of Jordan
-
Menoufia University
-
Université du Sousse
-
University of Khartoum
-
Université de la Manouba
-
Université Saint Joseph de Beyrouth
-
University of Dammam
-
King Faisal University
-
Université Libanaise
-
Qassim University
-
Beni-Suef University
-
Université Mohammed V Agdal
-
Sohag University
-
Helwan University
TOP UNIVERSITIES IN ASIA
-
University of Hong Kong
-
Tel Aviv University
-
Hebrew University of Jerusalem
-
National University of Singapore
-
Chinese University Hong Kong
-
Peking University
-
Seoul National University
-
Beijing Normal University
-
Nanyang Technological University
-
National University of Singapore
-
Tsinghua University
-
Peking University
-
Nanyang Technological University
-
Chinese University of Hongkong
-
University of Tokyo
-
Seoul National University
-
Kyoto University
-
Sungkyunkwan University
-
Fudan University
-
Zhejiang University
-
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
-
Yonsei University
-
Korea University
-
Tel Aviv University
-
National Taiwan University
-
Hebrew University of Jerusalem
-
Osaka University
-
Tohoku University
-
Koc University
-
Sabancı University
-
Nagoya University
-
Sun Yat-sen University
-
University of Malaya
-
University of Macau
-
Kyushu University
-
Chung-Ang University
-
Bar-Ilan University
-
Qatar University
-
Bilkent University
-
Hokkaido University
-
Hong Kong Baptist University
-
National Cheng Kung University
-
University of Tsukuba
-
Tianjin University
-
Ewha Womans University
-
Bogazici University
-
United Arab Emirates University
-
Soochow University
-
National Taiwan Normal University
-
American University of Beirut
-
Central China Normal University
-
Quaid-i-azam University
-
Xiamen University
-
Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur
-
Renmin University of China
-
East China Normal University
-
Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman
-
University of Haifa
Medicinal Chemistry
Application of New Hydrophobic Structures for Drug Design
Carboranes (dicarba-closo-dodecaboranes) are a class of carbon-containing polyhedral boron-amass mixes having incredible warm enduring quality and grand hydrophobic character. The carboranes were used in therapeutic science in the field of boron neutron catch treatment (BNCT) for fuse of expansive quantities of boron iotas into tumor cells. Be that as it may, little consideration has been paid to the conceivable utilization of carborane as a hydrophobic skeletal structure, in the field of medication outline. We have perceived the significance of hydrophobic collaboration in receptor-ligand complexation. The distinction of restricting constants between a ligand having an appropriate hydrophobic gathering and a ligand without such a gathering now and then achieves 100~10000 times. Along these lines, we concentrated on the outline and combination of atomic receptor modulators (retinoid agonists, retinoid opponents, estrogen agonists estrogen enemies) bearing a carborane confine as a hydrophobic skeletal structure for appraisal of the utility of icosahedral carborane as a hydrophobic part for sedate arrangement. Specialist arranged candidate estrogen-receptor-confining blends having carborane as a hydrophobic moiety and consolidated them.
The most strong compound bearing a carborane confine (BE120) displayed powerful movement in the focus scope of 1x10-10 - 1x10-8 M by luciferase journalist quality examine; its intensity is no less than 10-crease more noteworthy than that of estradiol. The compound likewise demonstrated intense in vivo consequences for the recuperation of uterine weight and bone misfortune in OVX mice. Improvement of the powerful carborane-containing estrogenic agonists portrayed here should yield novel hopeful helpful specialists, particularly specific estrogen receptor modulators. Moreover, the appropriateness of the circular carborane confine for authoritative to the pit of ER-LBD ought to give a premise to a comparable way to deal with creating novel ligands for other steroid receptors.
Perusing Histone Alterations
Turning qualities on and off is a complex procedure including correspondence between a wide range of kinds of proteins that collaborate with DNA.
These correspondences can go amiss, bringing about conditions like tumor. Specialists at the Cancer Center have revealed an irregular type of cross-talk between proteins that influence quality articulation, recommending better approaches for hindering metastasis in disease.
TRIM24 is an oncoprotein, which means it is found at a higher plenitude in numerous sorts of growth cells than in solid cells. Specialist thinks about what this protein does. Past research has demonstrated that TRIM24 is, in addition to other things, an epigenetic peruser. This implies it recognizes certain synthetic adjustments of histones - proteins around which DNA is snaked - and incites different proteins to change their conduct accordingly, bringing about an alternate example of qualities being turned on than if the histone had not been adjusted.
In the new investigation, discovered something bizarre. Did TRIM24 "read" histone adjustments, as well as the demonstration of perusing brought about TRIM24 itself being changed with a little protein tag called SUMO. As it were, perusing the message of the histone influenced the peruser to convey its own particular concoction message.
"This is the first occasion when that we are aware of that the (histone) itself is forcing a code on the modifiers or perusers,"
What does the expansion of SUMO to TRIM24 achieve? individuals performed trials to perceive how the qualities that TRIM24 turned on and off in tumor cells contrasted when TRIM24 didn't have SUMO connected.
They found that the SUMO-altered TRIM24 appeared to control qualities engaged with attachment between cells. This is essential since cell grip decides if tumor cells remain in one spot or can travel and metastasize through the body.
That is truly where these cell-grip atoms are becoming an integral factor, metastasis and relocation of growth cells,. Numerous proteins are engaged with bond, and TRIM24 killed a few and some on. In this manner it's not yet clear what net impact TRIM24 has on metastasis in malignancy patients. In any case, understanding that TRIM24 is engaged with this procedure gives specialists a place to hope to see how to stop it.
Meanwhile, the SUMO change likewise can be utilized as a conceivable marker in investigations of different sorts of potential new medications. Growth specialists are frequently keen on disturbing TRIM24's association with histones, keeping in mind the end goal to anticipate variant quality articulation. By following whether TRIM24 has SUMO appended, scientists can test whether a potential medication has effectively hindered the connection.
The energizing thing about adapting more about adjustments of TRIM24, for example, SUMO, is to have the capacity to create antibodies or different intends to recognize its essence,(This) might be a superior indicator of growths in beginning times or could be connected to potential for metastasis."
Another Association amongst Glucose and Lipid Control in Tumor Digestion
Scientist have recognized a catalyst that enables malignancy cells to make the building materials they have to rapidly multiply. Hindering this chemical could be a procedure to back off disease development, prompting more successful medicines.
While sound human cells get a large portion of the unsaturated fats and cholesterol they have to fabricate their cell layers from the circulation system, disease cells can't sit tight for their building materials to be conveyed by this course. Rather, growth cells as often as possible increase the action of the chemicals engaged with combining lipids right in the cell.
One of these groups of compounds is the sterol administrative component restricting proteins, or SREBPs. SREBPs go into cell cores and turn on qualities engaged with lipid generation, typically because of particular signs. In some tumor cell lines, including certain liver, colon and bosom growths, a specific SREBP called SREBP1a is overactive.
Reasearch observed that SREBP1a could be overactive in growth cells because of another chemical, pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2). PKM2 was adventitiously likewise known to be associated with providing hungry malignancy cells with surplus vitality through an alternate instrument: by synthetically adjusting a little atom called pyruvate amid glucose digestion. In the new examination, the specialists demonstrated that PKM2 was likewise ready to adjust SREBP1a.
PKM2, manages lipid digestion. So really we saw this is another association between a glucose digestion controller and a lipid digestion controller. In disease cells, both turn out to be unusually enacted.
Whenever PKM2 and SREBP1a connect, the SREBP1a turns out to be more steady, the investigation appeared. This enables SREBP1a to turn on qualities engaged with lipid amalgamation. Utilizing a little protein that could hinder the cooperation, the creators could stop the overabundance lipid generation and back off tumor cell development.
The tumor cells turn out to be particularly touchy; despite the fact that they can suck up loads of glucose, they can't make the building squares of the cell layer. In the event that joined with another medication, at that point this is a potential helpful approach.
The approach is promising on the grounds that it targets proteins that are not profoundly communicated in sound cells. On the off chance that malignancy cell development could be backed off by obstructing this pathway, patients may require bring down measurements of the lethal medications that really execute the growth cells, and along these lines encounter less symptoms.
Medicinal Chemistry Research
Research is a particular procedure used to think about and find out about substances. Normally directed as an undertaking, there are a few research themes led by restorative scientists.
Plants can assume an imperative part amid the medication disclosure and improvement period of therapeutic science. Plants have been utilized as restorative operators for a wide assortment of purposes, for example, a home grown solution for colds or sicknesses. In restorative science, analysts work to decide how certain properties of a plant can be utilized as a therapeutic operator to enhance general wellbeing and prosperity.
Understanding the positive therapeutic effect of plants on human wellbeing has affected medication revelation. For instance, opium, the characteristic compound found in the poppy seed plant, has been utilized since old circumstances. At the turn of the nineteenth century, restorative scientists found that morphine could be secluded from this plant-based operator to all the more successfully treat individuals' dreadful a throbbing painfulness.
Another case that features the significance of plant-based therapeutic science is the exploration chip away at drain thorn. This herb has been utilized as a solution for some years to mend diseases regularly connected with the liver, kidney and gallbladder. Research has demonstrated that drain thorn contains a specific specialist called a flavonoid. Flavonoids are a sort of compound discharged from plants. Restorative science based research has distinguished that flavonoids may add to the capable therapeutic utilization of drain thorn in treating liver harm.
ABC Transporters are Entrancing Natural Nanomachines
An examination group could depict with nuclear detail how particles are transported through organic films. PC reenactments and spectroscopic investigations gave bits of knowledge into crafted by alleged ABC transporters. These proteins assume a vital part in the medication protection of tumor cells and microorganisms.
"ABC transporters are interesting natural nanomachines," says leader of the Molecular Simulation examine gathering. These proteins couple the authoritative and substance cleavage of ATP particles, the compound vitality unit of the cell, with the vehicle of atoms through natural layers.
Protection of tumor cells and microscopic organisms
A specific normal for the alleged ABC exporters is that they transport an extensive variety of atoms out of the cell: from lipids and peptides to chemotherapeutic specialists. "ABC exporters thusly assume an essential part, incorporating concerning multi-tranquilize protection of malignancy cells and anti-infection protection of microbes".
The examination bunches are joined point by point PC reproductions with spectroscopic trials to reveal insight into the useful component of an ABC exporter in nuclear detail.
Seek after new treatment approaches
"Our outcomes demonstrate how the official of ATP atoms actuates basic changes in the transporter that are eventually required to help substrate particles through the film," clarifies Research group.In the long haul, be that as it may, these discoveries could add to the improvement of new restorative methodologies.
Enzyme Catalysis: Make and Break Amygdalin Hydrogelators for Hydrophobic Drugs
We report a novel approach for the controlled conveyance of a mitigating, chemopreventive medication by a catalyst activated medication discharge system by means of the corruption of epitomized hydrogels. The hydro-and organogelators are orchestrated in significant returns from sustainable assets by utilizing regioselective chemical catalysis, and a known chemopreventive and calming drug, i.e., curcumin, is utilized for the model investigation. The arrival of the medication happened at physiological temperature, and control of the medication discharge rate is accomplished by controlling the protein focus and additionally temperature. The side-effects framed after the gel debasement were described and unmistakably exhibited the site specificity of corruption of the gelator by compound catalysis. The present approach could have applications in creating financially savvy controlled medication conveyance vehicles from sustainable assets, with a potential effect on pharmaceutical research and sub-atomic plan and conveyance methodologies.
Carbon Nanotubes in Drug Design and Discovery
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have been proposed and effectively investigated as multipurpose inventive bearers for tranquilize conveyance and indicative applications. Their flexible physicochemical highlights empower the covalent and noncovalent presentation of a few pharmaceutically significant substances and take into consideration balanced outline of novel competitor nanoscale builds for tranquilize improvement. CNTs can be functionalized with various practical gatherings to convey all the while a few moieties for focusing on, imaging, and treatment. Among the most fascinating cases of such multimodal CNT develops depicted in this Account is one conveying a fluorescein test together with the antifungal medication amphotericin B or fluorescein and the antitumor operator methotrexate. The natural activity of the medication in these cases is held or, as on account of amphotericin B builds, upgraded, while CNTs can diminish the undesirable poisonous quality of the medication managed alone. Ammonium-functionalized CNTs can likewise be viewed as extremely encouraging vectors for quality encoding nucleic acids. Surely, we have framed stable buildings between cationic CNTs and plasmid DNA and showed the upgrade of the quality restorative limit in contrast with DNA alone. Then again, CNTs conjugated with antigenic peptides can be produced as another and powerful framework for engineered immunization applications. What makes CNTs very one of a kind is their capacity, first appeared by our gatherings in 2004, to latently cross films of a wide range of sorts of cells following a translocation system that has been named the nanoneedle component. In that way, CNTs open countless conceivable outcomes for future medication disclosure in light of intracellular focuses on that have been difficult to reach until today. Besides, enough functionalized CNTs as those appeared in this Account can be quickly dispensed with from the body following foundational organization offering further encouragment for their improvement. CNT discharge rates and aggregation in organs and any reactivity with the insusceptible framework will decide the CNT security profile and, therefore, any further pharmaceutical advancement. Alert is prompted about the requirement for deliberate information on the long haul destiny of these extremely fascinating and flexible nano-protests in relationship with the kind of CNT material utilized. CNTs are bit by bit plyaing a greater and more essential part in the rising field of nanomedicine; in any case, we have to ensure that the immense open doors they offer will be converted into attainable and safe builds to be incorporated into tranquilize disclosure and improvement pipelines.
Influence of Renal Impairment on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Oral Dabigatran Etexilate
Dabigatran etexilate is an oral direct thrombin inhibitor in clinical change for the neutralizing activity and treatment of thromboembolic issue. Following oral organization, dabigatran etexilate is quickly assimilated and changed over into its dynamic shape, dabigatran. The point of this examination was to research the impact of renal impedance on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dabigatran following organization of a solitary oral dosage of dabigatran etexilate in subjects with renal disability (150 mg) or end-arrange renal infection (ESRD) on support haemodialysis (50 mg).
This open-mark, parallel-gathering, single-focus consider enlisted 23 subjects with gentle, direct or serious renal hindrance (creatinine freedom >50 to ≤80, >30 to ≤50 and ≤30 mL/min, individually), 6 patients with ESRD and 6 solid subjects. Blood and pee tests were gathered up to 96 hours in the wake of dosing for assurance of dabigatran pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters.
Contrasted and the qualities in sound subjects, the zone under the plasma fixation time bend from time zero to boundlessness (AUC∞) values were 1.5-, 3.2-and 6.3-overlay higher in subjects with gentle, direct and extreme renal disability. Changes in the most extreme plasma fixation (Cmax) were unobtrusive, and an opportunity to come to the Cmax was unaltered. In subjects with serious renal weakness, the mean terminal end half-life was multiplied (28 hours versus 14 hours for control). The AUC for prolongation of pharmacodynamic parameters (the actuated halfway thromboplastin time and ecarin thickening time) expanded in accordance with the pharmacokinetic changes. In patients with ESRD, the measurement standardized AUC∞ was roughly double the incentive in the control gathering. Haemodialysis expelled 62– 68% of the measurements. Dabigatran etexilate was very much endured in all gatherings.
Introduction to dabigatran is expanded by renal weakness and corresponds with the seriousness of renal brokenness. A diminishing in the measurements and additionally an expansion in the organization interim in these patients might be suitable. In patients with ESRD, dabigatran can be halfway expelled from the plasma by haemodialysis.
Synthesis of C-coordinated O-carboxymethyl Chitosan Metal Complexes and Evaluation of their Antifungal Activity
In light of a buildup response, a chitosan-subordinate bearing amino pyridine amass was readied and in this way took after by coordination with cupric particles, zinc particles and nickel particles to incorporate chitosan metal edifices. The figurings utilizing the thickness practical hypothesis (DFT) demonstrate that the copper particles and nickel particles experienced dsp2hybridization, the zinc particles experienced sp3 hybridization, and they all shaped a coordination security with the carbon molecule in the p-π conjugate gathering. The antifungal properties of O-CSPX-M against Phytophthora capsici (P. capsici), Verticillium alboatrum (V. alboatrum), Botrytis cinerea (B. cinerea) and Rhizoctonia solani (R. solani) were likewise tested. Evidently, chitosan metal buildings demonstrated upgraded antifungal movement against four growths at the tried fixations contrasted with that of chitosan. It was demonstrated that Cu buildings can hinder the development of P. capsici 100%, and Ni edifices can repress the development of B. cinerea77.1% at a centralization of 0.4 mg/mL and 0.2 mg/mL, separately. The pot analyze likewise confirmed the outcome. Moreover, the phytotoxicity test demonstrated that O-CSPX-M had no conspicuous poisonous quality on wheat clears out. This sort of edifices may speak to as an appealing course for substance alterations of metal fungicides.
Pharmacogenomics-Drug Targets and Side Effects
It is very much perceived that diverse patients react in various approaches to a similar solution. These distinctions are regularly more noteworthy among individuals from a populace than they are inside a similar individual at various circumstances (or between monozygotic twins). The presence of huge populace contrasts with little intrapatient changeability is reliable with legacy as a determinant of medication reaction; it is assessed that hereditary qualities can represent 20 to 95 percent of fluctuation in tranquilize aura and impacts. Albeit numerous nongenetic factors impact the impacts of pharmaceuticals, including age, organ work, attendant treatment, sedate cooperation, and the idea of the malady, there are currently various cases of cases in which interindividual contrasts in tranquilize reaction are because of grouping variations in qualities encoding drug-processing chemicals, medicate transporters, or medication targets. Not at all like different components affecting medication reaction, acquired determinants by and large stay stable all through a man's lifetime.
Clinical perceptions of acquired contrasts in tranquilize impacts were first recorded in the 1950s, offering ascend to the field of Pharmacogenetics, and later pharmacogenomics. Despite the fact that the two terms are synonymous for every single pragmatic reason, pharmacogenomics utilizes far reaching ways to deal with clarify the acquired premise of contrasts between people in the reaction to drugs.
In excess of 1.4 million single-nucleotide polymorphisms were distinguished in the underlying sequencing of the human genome, with more than 60,000 of them in the coding district of qualities. Some of these single-nucleotide polymorphisms have just been related with considerable changes in the digestion or impacts of medicines, and some are presently being utilized to anticipate clinical reaction Because most medication impacts are controlled by the interchange of a few quality items that impact the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of solutions, incorporating acquired contrasts in tranquilize targets (e.g., receptors) and medication manner (e.g., processing compounds and transporters), polygenic determinants of medication impacts have turned out to be progressively vital in pharmacogenomics. In this survey, we center around the helpful results of acquired contrasts in tranquilize air and medication targets. A going with review12 centres around the Pharmacogenetics of medication digestion. This survey isn't intended to be thorough; rather, clinically applicable cases are utilized to delineate how pharmacogenomics can give sub-atomic demonstrative strategies that enhance medicate treatment.
Drug Delivery and Nanoparticles
The usage of nanotechnology in solution and more especially steady transport is set to spread rapidly. At show various substances are under investigation for sedate movement and more especially for illness treatment. The kind of dangers that are displayed by using nanoparticles for sedate movement are past that acted by customary risks constrained by chemicals in set up transport structures. For nanoparticles the learning on particle toxic quality as gained in internal breath lethality exhibits to the way business measures to inspect the potential risks of nanoparticles. The toxicology of particulate issue contrasts from toxicology of substances as the making chemical(s) could possibly be dissolvable in characteristic systems, in this way influencing unimaginably the potential presentation of various inside organs. This may shift from a truly high neighbourhood presentation in the lungs and a low or neglectable introduction for other organ frameworks after inner breath. Nevertheless, held species may in like manner affect the potential harmful nature of the took in particles. For nanoparticles the situation is various as their size opens the potential for crossing point the diverse regular deterrents inside the body. From a positive viewpoint, especially the likelihood to cross the blood Brain limit may open new courses for sedate transport into the cerebrum. Moreover, the nano measure in like manner considers access into the cell and diverse cell compartments including the centre. A gigantic number of substances are beginning at now under scrutiny for the masterminding of nanoparticles for cure transport, moving from normal substances like egg whites, gelatine and phospholipids for liposomes, and more substances of a blend nature like various polymers and strong metal containing nanoparticles. Obviously, the potential correspondence with tissues and cells, and the potential toxic quality, altogether depends upon the genuine structure of the nanoparticle detailing. For such testing the lessons picked up from particle risk as associated in internal breath toxicology may be valuable. Disregarding the way that for pharmaceutical use the present necessities have all the earmarks of being agreeable to distinguish most of the unpleasant effects of nanoparticle plans, it can't be typical that all parts of nanoparticle toxicology will be perceived. Thusly, likely additional more specific testing would be required.
Stereochemistry: a source of problems in Medicinal Chemistry: Bio-organic and Medicinal 2018
Stereochemistry is the study mainly focuses on stereoisomers and spans the complete scenario of organic, bioorganic, inorganic, physical, biological and particularly supramolecular chemistry. Stereochemistry includes strategies for determination and describing these different types of relationships. The result of the physical or biological properties these relationships impart upon the molecules in question, and also the manner in which these relationships influence the reactivity of the molecules.
Mainly Isomers are:
i. Enantiomers: Stereoisomers which are mirror images
ii Diastereoisomers: Stereoisomers which do not mirror images
Drug Delivery Techniques: Importance of Novel Drug Delivery System: Bio-organic and Medicinal 2018
Drug delivery is the method of intended a pharmaceutical dosage form to produce a therapeutic effect for human or animal use. It is an integrated concept with dosage form and route of administration. Nasal and pulmonary routes of drug delivery techniques are gaining importance for the treatment of human diseases. These methods are concerned with the drug release profile, absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination for the improvement of the product viability, safety and patient convenience and compliance. To lower the drug degradation, adverse effects, toxic effects and side effects. To enhance drug compound bioavailability and bioequivalence to prevent harmful toxic-effects. Various types of drug delivery and drug targeting techniques are currently under development
· Novel Drug Delivery System
· Polymeric drug delivery technique
· Drug delivery using Nanotechnology
· Transdermal drug delivery system
· Micro emulsifying drug delivery
· Liposomal and Target Delivery System
· Drug carrier delivery system
· Magnetic drug delivery
· Bioadhesive drug delivery systems
Novel drug delivery system Evolution of an existing drug molecule from a conventional form to a novel delivery system can significantly improve its performance in terms of patient compliance, safety and efficacy. A proper designed Novel Drug Delivery System will be a major advance in solving the problems related towards the release of the drug at a specific site with the specific rate. In the form of a Novel Drug Delivery System, an existing drug molecule can get a new life. The need for delivering drugs to patients efficiently and with fewer side effects and adverse effects has prompted pharmaceutical companies to engage in the development of new drug delivery system. New ideas on controlling the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, non-specific toxicity, immunogenicity, site-specific delivery, biorecognition, improved Bioavailability, Bioequivalence and efficacy of drugs were generated. These are also called drug delivery systems (DDS), which are based on p mainly polymer Chemistry, Pharmaceutical Chemistry, bioconjugate chemistry, and Medicinal Chemistry. To reduce drug degradation, and prevent from harmful side-effects and adverse effects, increasing drug bioavailability and the fraction of the drug accumulated in the required zone.
Importance of Chirality in Development of Pharmacokinetic Study
Chiral carbon is known as the carbon with the 4 different groups. The presence of a chiral center in drugs and bioactive agents, in general, implies large differences for the enantiomers both in the activity in the strict sense and for metabolic conversion and pharmacokinetics in general. Structural requirements for the biological activity often imply the presence of one or more chiral centers in the drug. Many of them are marketed as racemates. The enantiomers must, particularly from the biological point of view, be regarded as different substances. The neglect of stereochemistry in the development and applications and is a source of problems in pharmacokinetics. Symmetry is a very common phenomenon in nature on the molecular level. Chirality is not a requirement for bioactivity but in those cases, and there are many in which a chiral center is present in the bioactive molecules. This Stereochemistry mainly useful in the nomenclature of the active pharmaceutical ingredients, drug metabolism, and drug monitoring.
· Molecular chirality and enantiomers
· Properties of chiral molecules and optical activity
· The Cahn Ingold Prelog RS notational system
· Physical properties of enantiomers
· Stereogenic center
Past Conference Report
Drug Discovery Congress 2017
We gratefully thank all our wonderful Speakers, Conference Attendees, Students, Media Partners, and Associations for making Drug Discovery Congress 2017 Conference the best ever!
The 4th Annual Congress on Drug Discovery & Designing, hosted by the Conference was held during July 03-04, 2017 at Bangkok, Thailand based on the theme “Accelerate Drug Discovery and identify new methods of Drug Design". Benevolent response and active participation were received from the Organizing Committee Members along with Scientists, Researchers, Students and leaders from various fields of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug Discovery, who made this event a grand success.
ME Conferences expresses its gratitude to the conference Moderator, namely Dr.Zvi Naor for taking up the responsibility to coordinate during the sessions. We are indebted to your support.
The conference was initiated with the Honourable presence of the Keynote forum. The list includes:
· Chi Hin Cho, Chinese University of Hong Kong, China
· Zvi Naor, Tel Aviv University, Israel
· Suparerk Borwornpinyo, Mahidol University, Thailand
The meeting reflected various sessions, in which discussions were held on the following major scientific tracks:
· Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery
· Cheminoinformatics Drug Discovery
· Clinical Trials and Regulatory Affairs
· Perspective in Drug Discovery
· Pharmaceutical Research & Development
· CNS Drug Discovery
· Diabetes and Obesity Drug Discovery
· Drug Delivery & Targeting
· HIV Drug Discovery & Research
· Inflammation and Immunology·
· Nutraceutical Drug Discovery and Therapy
· Recent Advances in Spectroscopy & CADD
· Regenerative Medicine
· Drug Designing
· Insilco Drug Discovery
· Proteomics & Bioinformatics
Thank all our expert presenters from all around the world which includes various outside experts, University representatives and other eminent researchers who supported the conference by facilitating the discussion forums.
With the grand success of Drug Discovery Congress 2017, Conferences take the immense pleasure to announce the “World Congress on Bio-organic and Medicinal Chemistry ” to be held during November12-13,2018 at Dubai, UAE.
Conference Highlights
- Computational Chemistry
- Medicinal Biochemistry
- Chemical Biology
- Structural & Molecular Biochemistry
- Biological Drug Targets
- Drug Design, Discovery and Development
- Drug delivery Techniques
- New Trends in Medicinal Pharmacy
- Global Chemical Analysis
- Organic Chemistry in Today’s Life
- Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Pharmacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics
- Organic Chemical Engineering
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | November 12-13, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by


















































